Ankle Injury Treatment Melbourne
What is Ankle Sprain?
One of the most common ankle injuries is a lateral sprain. An ankle sprain occurs when the ankle rolls towards the outside of the foot from a force being applied to the ankle joint, causing excessive movement at the joint.
There are three ligaments often injured or torn in a lateral ankle sprain. Individuals immediately become aware of the sprain as they may hear an audible ‘snap’ or ‘pop’, due to the tearing or stretching of those ligaments.
Causes
Sports involving jumping, turning and twisting are particularly vulnerable to ankle sprains. Pain will be felt on the outside of the ankle and may begin to swell and form a bruise along the outside of the ankle and foot.
Risk factors for ankle sprains include:
- Previous injury
- Poor footwear
- Poor strength and stability of the ankle Sudden change in direction
- Increased age
Other common causes of ankle pain may include ankle fractures, Achilles tendonitis, gout, arthritis, or nerve impingement. Ankle pain may also result from underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, neuropathy or peripheral artery disease.
It is important to identify the specific cause of ankle pain through proper diagnosis and assessment by a healthcare professional, as the appropriate treatment may differ depending on the underlying cause.
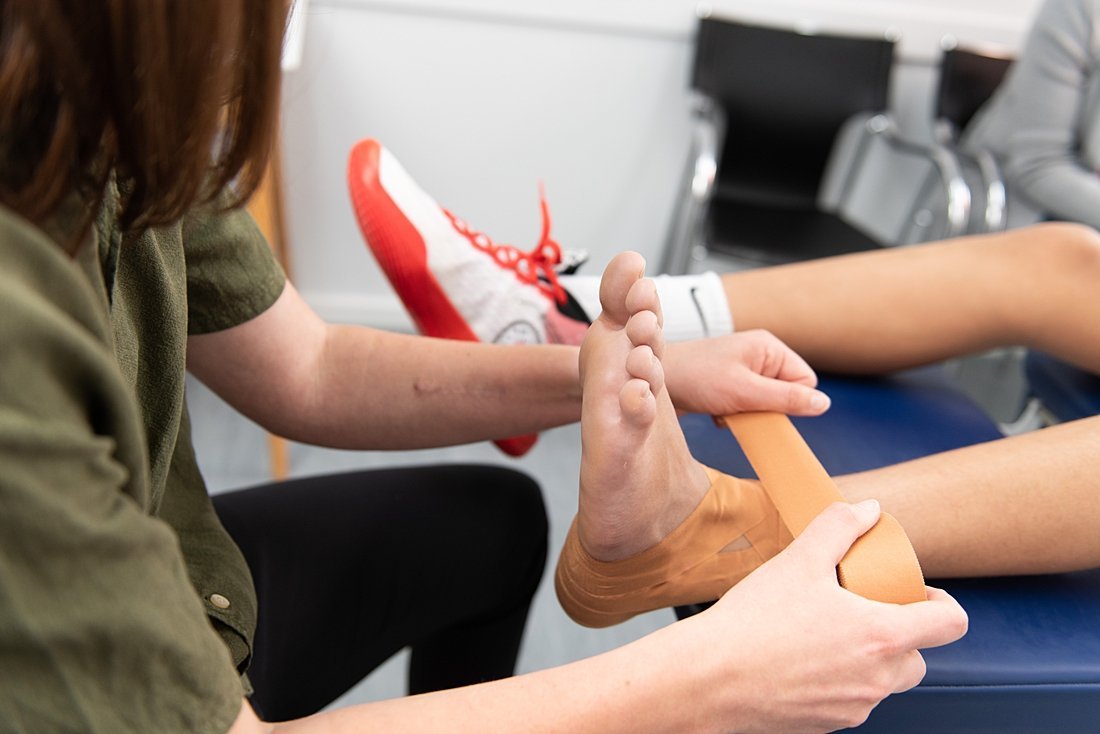


Treatment
The immediate treatment of any soft tissue injury consists of the RICER protocol – rest, ice, compression, elevation and referral.
RICE protocol should be followed for 48 – 72 hours. The aim is to reduce the bleeding and damage within the joint.
The No HARM protocol should also be applied – no heat, no alcohol, no running or activity, and no massage. This will ensure decreased bleeding and swelling in the injured area.
Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) may be used to control pain and inflammation. Consult your Podiatrist or Pharmacist prior to using medication.
In severe cases where the ankle injury involves significant pain or deformity, emergency treatments for ankle injuries may include surgical intervention or immobilization with a cast. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if any of these symptoms are present.
It is important to note that emergency treatments for ankle injuries, such as surgery or immobilization with a cast, should only be performed by a trained medical professional. Delaying treatment can result in prolonged recovery time and potentially long-term damage to the ankle.
Diagnosis and Assessment of Ankle Sprains by your Podiatrist
DIAGNOSIS
Highett Podiatry can examine the injured ankle to determine which ligaments are torn and to what extent they are damaged. Sprained ankles are divided into grades 1 – 3, depending on their severity.
ANKLE INJURY ASSESSMENT
Sprains are graded on a scale of 1 to 3 (mild, moderate, and severe), depending on the degree of tearing to the ligaments. In most cases, x-rays are performed to rule out a fracture or dislocation.
Grade and Description
1 (Mild)
- Minor tear
- Minimal pain
- Little or no joint instability
- Mild pain with weight bearing activities
- Slight loss of balance
2 (Moderate)
- Some tearing of the ligaments fibres
- Moderate to severe pain
- Moderate instability of the joint
- Swelling and stiffness
- Pain with weight bearing activities
- Poor balance
3 (Severe)
- Complete tear of the ligament
- Severe pain followed by the minimal pain
- Gross instability of the joint
- Severe swelling
- Possible pain with weight bearing
- Poor balance
Treatment
Our podiatrists can immobilise your injury with strapping, bracing or by placing you in a CAM walker. We also may prescribe crutches to aid in the healing process. Soft tissue therapy in the form of ultrasound, deep tissue massage and dry needling is also available.
X-RAY AND ULTRASOUND REFERRAL
If required, your podiatrist can refer you for X-rays, ultrasounds and other radiology scans. X-rays and ultrasounds referred by podiatrists are eligible to be billed through Medicare and can be bulk billed. Please note MRI scans will incur a fee, however our podiatrists can still provide a referral if it is indicated.
REHABILITATION
Research shows that early mobilisation and the use of specific modalities on ankle sprains result in better outcomes. Most ankle injuries heal within 2-6 weeks, although a severe sprain can take up to 12 weeks. Appropriate rehabilitation is crucial in preventing the injury reoccurring and reducing long-term ankle instability. Our customised rehabilitation programs may include exercises for strengthening and stabilising the ankle joint, bracing or strapping to provide support through the process.
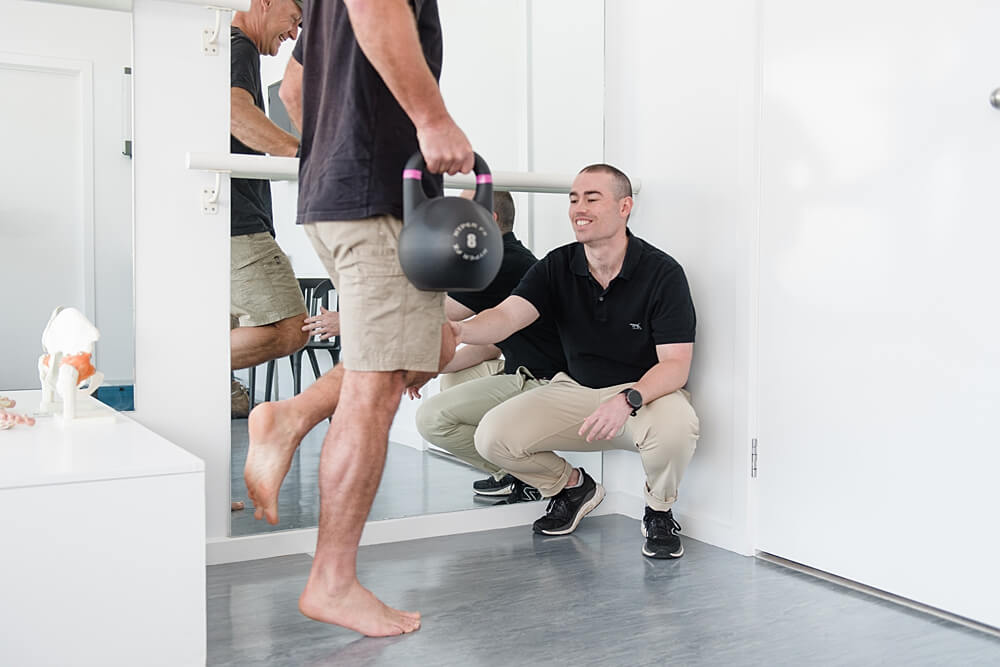

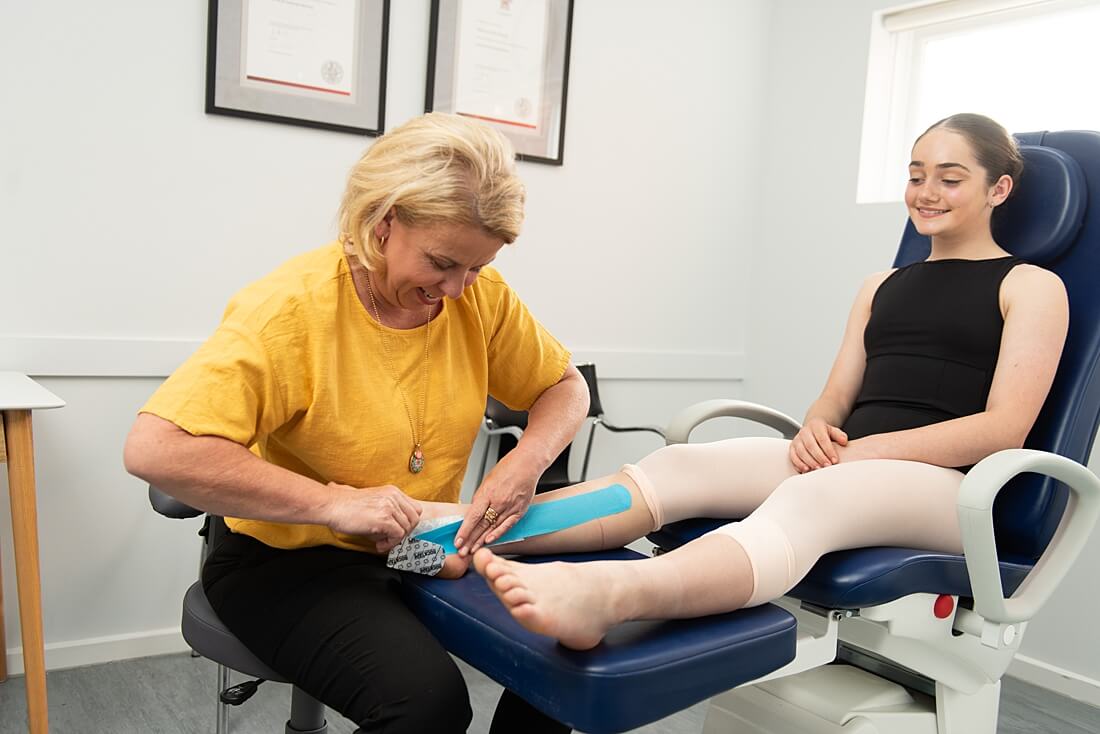
REHABILITATION AND RETURN TO PLAY
Most ankle sprains heal within 2 to 6 weeks, however severe sprains many take as long as 12 weeks.
A comprehensive rehabilitation program minimises the chance of the injury recurring and includes flexibility, balance, stretching, strengthening and sport specific exercises. During this time, taping or bracing the ankle may be prescribed to provide support until full function is regained. If, while performing a rehabilitation exercise, ankle joint pain or discomfort is experienced, stop immediately and reconsult a sports medicine professional.
Patients with significant ligament injuries (Grade 2 or 3) are advised to use bracing or protective taping when playing sport for a minimum of 6 to 12 months post injury.
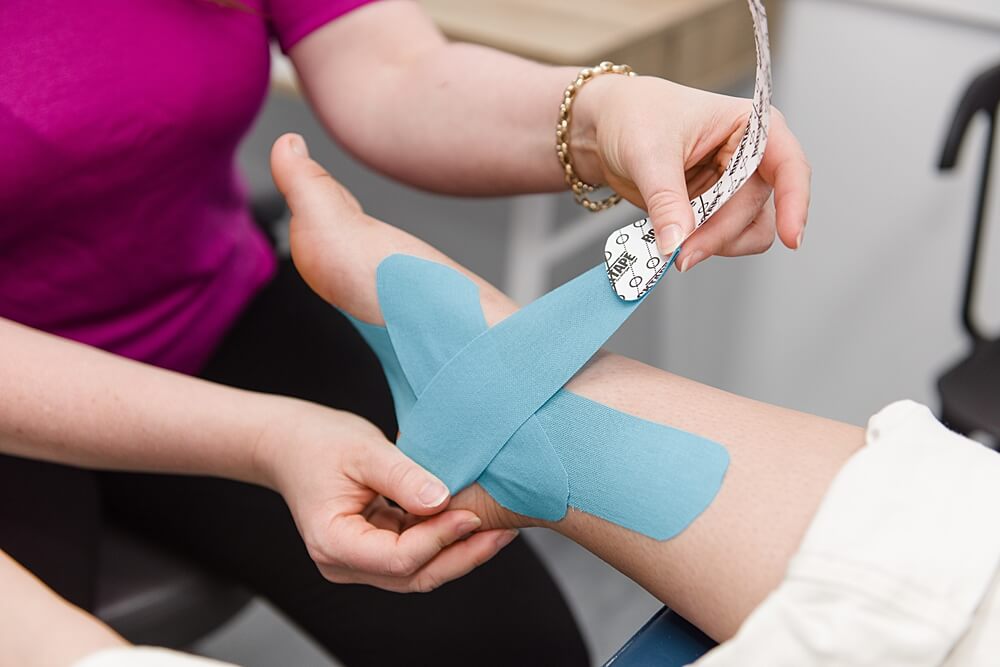
Ankle Strapping
Ankle sprains are one of the most common injuries of the foot. They are particularly common in sports that involve change of direction or jumping, with high incidences reported in soccer, netball, AFL & basketball. Ankle strapping is commonly used in athletes who have a previous history of ankle sprain injuries.
How can Ankle Strapping help?
Strapping of the ankle provides stability to the joint and reduces the amount of motion available at the ankle joint. The strapping acts as a support mechanism to surrounding ligaments to ensure the ankle does not move outside its comfortable range. Strapping also provides proprioceptive feedback to the body to encourage the foot to stay in the correct alignment.
Strapping allows the athletes to return to sport earlier following an injury and also provides confidence to the athlete that the ankle is supported.
Chronic Ankle Pain
Chronic ankle pain can be due to numerous causes including poor alignment, abnormal stresses, previous injury, osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis and compression injuries.
Other Types of Ankle Injuries
Strains
A strain is an injury to a muscle or tendon that can occur when the ankle is overused or subjected to sudden force. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and stiffness. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as physical therapy to regain strength and flexibility.
Fractures
A fracture is a break in one or more of the bones in the ankle. Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty walking. Treatment depends on the severity of the fracture and may involve immobilisation with a cast or brace, surgery, and physical therapy.
Dislocations
A dislocation occurs when the bones in the ankle are forced out of their normal position. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and deformity of the ankle joint. Treatment involves realigning the bones and immobilising the ankle with a cast or brace, as well as physical therapy to regain strength and flexibility.
Always Consult A Trained Professional
The information in this resource is general in nature and is only intended to provide a summary of the subject matter covered. It is not a substitute for medical advice and you should always consult a trained professional practising in the area of medicine in relation to any injury or condition. You use or rely on information in this resource at your own risk and no party involved in the production of this resource accepts any responsibility for the information contained within it or your use of that information.
